How does a Belt Driven Air Compressor Work?
Belt driven air compressors are made of a system where an electric motor spins a belt, which in turn rotates a compressor pump. This mechanism is quite similar to how a car engine powers the various parts of the car. By leveraging the rotational kinetic energy from the motor, the belt powers the compressor to take in air, pressurize it, and output it with force, making your pneumatic tools and processes possible.
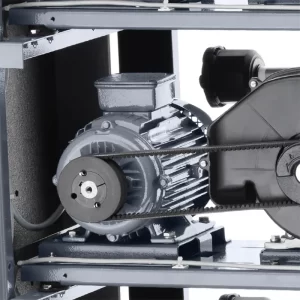
What is the principle of air compressor?
The working principle of an air compressor revolves around converting power from an electric motor, diesel, or gasoline engine into potential energy stored in pressurized air, also known as compressed air. At its core, an air compressor takes in atmospheric air at ambient pressure, uses a method to compress it (which could involve pistons, rotors, or screws), and then stores it in a tank at a higher pressure.
This process not only reduces the volume of the air but also increases its pressure, creating a useful energy reserve that can be used in a variety of applications. In essence, the air compressor functions by forcing more and more air into a storage tank, increasing the pressure until it reaches a pre-set limit, at which point the compressor shuts off. The pressurized air is then held in the tank until called into use for tasks ranging from inflating tires to powering pneumatic tools.
What is the difference between direct driven and belt-driven?
The primary distinction between direct driven and belt-driven air compressors lies in their mechanism of power transmission from the motor to the compressor. Direct driven air compressors feature a direct connection between the motor shaft and the compressor, meaning the compressor’s rotor spins at the same speed as the motor. This direct coupling allows for a more efficient power transfer, often resulting in higher efficiency, reduced maintenance due to fewer moving parts, and a smaller footprint since there is no need for belts or pulleys.
On the other hand, belt-driven air compressors utilize a system of belts and pulleys to connect the motor to the compressor. This setup allows for flexibility in adjusting the speed of the compressor by changing pulley sizes, enabling the compressor to run at a lower speed than the motor. Belt-driven systems can be less efficient due to belt slippage and the need for more frequent maintenance, such as belt tension adjustments and replacements.
What is the difference between belt drive and direct drive air compressors?
The difference between belt drive and direct drive air compressors, as outlined, boils down to their power transmission method. Belt drive air compressors offer flexibility and are often chosen for applications where variable speeds are beneficial. They are ideal for settings that don’t demand continuous, high-speed operation and where the ability to adjust speeds can result in improved energy efficiency and reduced wear on the compressor.
Direct drive air compressors, in contrast, are known for their simplicity and reliability. With fewer moving parts, they typically require less maintenance over their lifespan and are more compact, making them suitable for environments where space is at a premium.
Which style of compressor uses belts?
The style of compressor that utilizes belts is the belt drive air compressor. This design depends on a system of belts and pulleys to connect the motor with the compressor, allowing for adjustments in speed through the alteration of pulley sizes. This flexibility can be particularly advantageous in applications where the compressor does not need to operate at full capacity continuously, as it can lead to energy savings and potentially extend the lifespan of the compressor by operating it under less strain.
However, the reliance on belts also introduces certain maintenance requirements, such as regular checks and adjustments for belt tension and alignment, as well as replacing worn belts to ensure efficient operation and prevent downtime.
What is the advantage of a belt-driven air compressor?
The primary advantage of a belt-driven air compressor lies in its versatility and energy efficiency. By leveraging a belt and pulley system, these compressors can easily adjust their operating speed to match the current demand. This adaptability not only allows for significant energy savings by avoiding the need to run the compressor at full capacity at all times but also reduces the overall wear and tear on the compressor’s components.
The inherently quieter operation of belt-driven models compared to their direct drive counterparts makes them more suitable for environments where noise levels are a concern. Although maintenance requirements are somewhat higher due to the belts and pulleys, the benefits of lower operating costs and flexibility often outweigh these considerations for many users.
Comparing Belt Driven Compressors to Direct Drive Compressors
The best way to compare machines is by using measurable metrics that gauge their performance. In this section, we will compare belt-driven air compressors to their direct drive and screw counterparts.
1. Efficiency
Direct-driven air compressors are known for their high efficiency. This is because a direct driven design allows for maximum power transfer from the motor to the compressor with minimal loss, which is not the case with belt-driven compressors.
However, with direct-drive compressors, any issues with the motor can directly impact the compressor’s performance. This is less of a concern with belt driven models, as the belt acts as a buffer between the two components.
2. Noise Levels
Compared to other types of air compressors, belt-driven models are significantly quieter. This is largely due to the fact that the belt absorbs much of the vibration that would otherwise be transmitted through the structure of the machine.
Conversely, direct drive air compressors, which lack a belt, tend to be much noisier as the vibrations from the motor directly translate to the compressor.
3. Maintenance
Direct air compressors are easier to maintain than belt-driven air compressors. This is because the direct drive design eliminates belts and pulleys which can wear out over time and require replacement.
4. Versatility
Belt driven air compressors are also versatile. They can be used in a variety of settings, from industrial applications to home use. Although they may not be as portable as smaller, direct-drive models due to their greater size, they make up for it with their adaptability and efficiency.
4. Cost
In terms of cost, belt-driven air compressors can be more expensive initially than their direct drive counterparts. However, when you factor in their efficiency, durability, and ease of maintenance, they often prove to be more cost-effective in the long run. Plus, the comfort of a quieter workspace can, for many, justify the additional upfront cost.
Choosing The Right Belt Driven Air Compressors

When selecting a belt-driven air compressor, there are many things to consider. Below are six things you might want to think about before making the decision to buy a belt-driven compressor. Typically, these are the metrics to look at when buying most types of air compressors.
The (CFM) rating
CFM is a rating that indicates the volume of air that a compressor can supply. Tools that require high volumes of air, like sanders or grinders, will need a compressor with a relatively high CFM rating.
The (PSI)
Most tools will require at least 90 PSI to operate, but some heavy-duty tools may require more. So, when buying a belt-driven compressor, ensure that the compressor you choose can meet this demand.
The Tank Size
A larger tank can store more compressed air, reducing the frequency with which the compressor has to run while a small tank will do the opposite. If you want a heavy-duty, continuous use, opt for a larger tank. For intermittent use or smaller tasks, a smaller tank will serve you just fine.
Source of Power
The power source of your air compressor can significantly affect its convenience and usability. Electric air compressors are generally more energy-efficient and quieter, whereas gas-powered models may offer more mobility in areas where electricity is not readily available.
Durability and Maintenance
As a rule of thumb, go for a model that’s built with high-quality, robust materials that can withstand heavy use. Also be sure to check the maintenance requirements. Some air compressors may come with oil-free designs, which reduce the need for regular maintenance, while some may require regular oil changes. Consider your usage needs and choose accordingly.
Cost and Warranty
Belt-driven air compressors can range in price from a few hundred dollars to thousands, depending on the size, features, brand, and quality. When considering cost, remember to balance it against the compressor’s performance and durability. Additionally, check for warranty coverage to ensure that you will be covered in case of any defects or malfunctions.
Safety Features
When working with air compressors, safety should always be a top priority. Look for models that come with essential safety features such as pressure relief valves, automatic shut-off switches, and thermal overload protection to prevent accidents and damage to the compressor.
Applications of Belt-Driven Air Compressors
Belt-driven air compressors find widespread use in a variety of sectors due to their advantageous attributes. Here, we delve into some of the primary applications where these machines prove exceedingly useful.
The Automotive Industry
Belt-driven air compressors are quintessential tools in car manufacturing and repair workshops. They power a wide range of pneumatic tools such as impact wrenches, spray guns, and sandblasters that are widely used in the automotive industry.
Moreover, their quiet operation makes the work environment pleasant, and their durability ensures that they can withstand the demanding conditions of an automotive workshop.
The Construction Industry
In the construction industry, these compressors play a vital role. They are used to power a variety of heavy-duty tools such as jackhammers, pneumatic drills, and concrete vibrators.
Their high efficiency, coupled with their durability, make them the perfect candidate for such rugged applications where reliability and performance are crucial.
Home Use
Even for home use, belt-driven air compressors can be quite handy. They can power a variety of tools, such as nail guns for home renovation projects or paint sprayers for home improvement tasks.
Their relatively quiet operation is a significant advantage in residential settings where noise may be a concern.
Industrial Manufacturing
In industrial manufacturing, belt-driven air compressors are integral to various processes. They can be used for applications such as powering production machinery, inflating tires in a production line, and even in the packaging process where compressed air is used to shape and seal plastic containers.
Agriculture
In the agricultural sector, these compressors are used in a variety of tasks, such as powering irrigation systems, pneumatic tools for maintenance work, and even in the process of crop dusting where compressed air is used to disperse pesticides or fertilizers over a field.
Conclusion
A belt-driven air compressor is an essential tool for various tasks such as providing reliable power for irrigation as well as powering pneumatic tools. Maintenance is essential to keep your belt-driven air compressor in top condition. Regularly check and change the oil, clean or replace filters, and inspect belts for wear and tear. These steps can help prevent breakdowns and extend the lifespan of your compressor.

