Air receiver tanks are also known as compressed air storage tanks. They play a pivotal role in the field of pneumatic systems as they act as temporary storage for compressed air, serving several important functions.
While storing the air, they stabilize pressure fluctuations, store excess air produced during periods of low demand, and provide a reserve during periods of high demand. Their role is so substantive that the efficiency of the entire pneumatic system could hinge on the capacity and performance of the air receiver tank.
From cooling and condensing air to reducing moisture and contaminants within the system, the influence of the air receiver tank cannot be overstated. In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of these tanks, their varieties, and their essential contribution towards the smooth running of pneumatic systems.
The Purpose and Function of Air Receiver Tanks
In a compressed air system, air receiver tanks serve as crucial elements that guarantee smooth operation. As buffers, they mitigate short-term demand spikes and avoid unnecessary cycle loading of the compressor, extending its life and improving efficiency. By serving as storage units, they ensure that during instances of high demand, there is a sufficient supply of compressed air to meet the requirements without causing system failure.
How Air Receiver Tanks Work
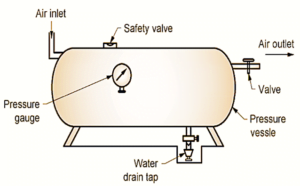
Air receiver tanks function as the lungs of a compressed air system, expanding and contracting based on the consumption and production of air. The compressor pumps air into the tank, thereby increasing the pressure. When the system demand is more than the compressor output, the tank releases the stored air to maintain the system pressure.
Simultaneously, the tanks hold back the air when the compressor’s output exceeds the system’s demand, reducing the compressor’s load. It’s this constant activity of storage and release that ensures the compressed air system’s continuous operation.
Types of Air Receiver Tanks
Vertical vs. Horizontal Air Receiver Tanks
Air receiver tanks primarily come in two orientations: vertical and horizontal. Vertical air receiver tanks are taller with a smaller base, making them ideal for workplaces with limited floor space. They’re commonly used in industrial settings where high amounts of stored energy are needed in a confined area. On the other hand, horizontal air receiver tanks, with their larger surfaces, provide a greater air surface area for cooling and are easier to maintain, as they allow for more comfortable access to the drain and pressure relief valves. However, they require more floor space and may not be suitable for compact spaces.
Wet vs. Dry Air Receiver Tanks
In addition to orientation, air receiver tanks can also be classified as wet or dry. Wet air receiver tanks are placed in proximity to the compressor. They store the air directly from the compressor which is usually hot and contains a large amount of moisture and oil that gets cooled and condensed inside these tanks. This cooling effect reduces the load on downstream dryers.
Dry receiver tanks, on the other hand, are placed after the air drying system. They store air that has already been dried and filtered, making them vital in applications where high-quality, contaminant-free air is required. By storing clean, dry air, these tanks help to ensure a steady supply of high-quality air, even during peak demand times.
Climate Considerations for Air Receiver Tanks
When it comes to air receiver tanks, climate can play a significant role in their performance and longevity. In areas with extreme temperatures, it’s essential to consider the impact of temperature fluctuations on the tank’s internal pressure. As temperatures fluctuate, so does the pressure inside the tank, which can lead to potential safety hazards if not monitored properly. Additionally, extreme cold temperatures can cause moisture to freeze inside the tank, reducing its efficiency and potentially causing damage.
On the other hand, in areas with high humidity levels, moisture can accumulate inside the tank, leading to potential rust and corrosion issues. Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial in these environments to ensure that the air receiver tank is functioning correctly and not posing a safety risk.
Safety Measures for Air Receiver Tanks
To ensure the safe and efficient operation of air receiver tanks, it’s essential to follow certain safety measures. These include regular inspections, maintenance, and testing of the tank’s pressure relief valves to prevent any potential overpressure situations. It’s also crucial to monitor the tank’s internal temperature and pressure regularly and address any abnormalities immediately.
Proper installation is also vital for safe operation. Air receiver tanks should be installed on a stable, level surface and secured according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Any piping or connections should also be inspected for leaks regularly.
In addition to these safety measures, it’s essential to follow all local regulations and codes when it comes to air receiver tanks. These regulations may vary by location, so it’s crucial to do thorough research and comply with all requirements to ensure the safe use of the tank.
How to Store Air Receiver Tanks Outdoor Safely [Tips for Outdoor Storage]

Most users prefer to have their air receiver tanks stored outside their buildings because of space limitations. However, outdoor storage presents its own set of challenges and safety concerns. Here are some essential tips for safely storing air receiver tanks outdoors:
- Choose a level and stable surface: The ground should be firm enough to support the weight of the tank, even when it’s full.
- Protect from direct sunlight: Exposure to direct sunlight can increase the temperature inside the tank, leading to potential hazards. It’s best to store the tank in a shaded area or use a cover.
- Protect from extreme weather conditions: Harsh weather conditions like rain, snow, and high winds can damage the tank or cause it to tip over. Ensure the tank is sheltered or protected with a sturdy cover during adverse weather.
- Inspect regularly: Outdoor storage exposes the tank to various elements that can cause damage or corrosion. Regularly inspect the tank for any abnormalities and address them immediately.
- Follow local regulations: Just like indoor storage, it’s essential to follow all local regulations and codes when storing air receiver tanks outdoors. This includes obtaining necessary permits and following proper installation guidelines.
Air Receiver Materials and Internal Lining
The type of material used to make an air receiver tank is also crucial and should be considered when choosing a storage location. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and composite materials. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to select the right material for your specific application.
Most tanks have internal linings that protect them from corrosion, increase longevity, and improve air quality. These linings are usually made of materials like rubber, epoxy, or glass-lined steel. Depending on the application and environment, certain linings may be more suitable than others.
Safety Precautions
Although air receiver tanks are designed to withstand high pressures and store compressed air safely, it’s essential to take proper precautions when handling them. Here are some general safety tips to keep in mind:
- Proper handling: When moving or installing an air receiver tank, ensure it is done carefully and with proper equipment. Follow manufacturer guidelines for installation and usage.
- Pressure relief valves: These are essential components that release pressure from the tank if it exceeds safe levels. Make sure they are regularly tested and functioning correctly.
- Drain valves: It’s crucial to regularly drain excess moisture and condensation from the tank to prevent corrosion and maintain air quality.
- Inspections: Regularly inspect the tank for any signs of damage, such as cracks or leaks. Address any issues immediately to prevent further damage or safety hazards.
- Maintenance: Follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance, including cleaning, lubricating, and replacing parts as needed.
Sizing and Placement
Selecting the right size and placement for your air receiver tank is crucial for efficient and safe operation. Factors like compressed air usage, pressure requirements, and available space should be considered when determining tank size. It’s also essential to place the tank in a well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
Air Receiver Tank Accessories
Below is an outline of common air receiver tank accessories and their purpose. These can enhance the functionality and safety of your tank.
- Pressure gauges: These provide a visual indication of the pressure inside the tank. Keeping an eye on the pressure levels can help prevent overfilling and potential hazards.
- Check valves: These one-way valves allow air to flow into the tank but prevent it from escaping when the compressor is not running.
- Pressure switches: These control the operation of the compressor by turning it on and off at designated pressure levels.
- Automatic drains: These drain valves can be set to release moisture automatically, preventing manual draining and saving time.
Certifications and Regulations
When purchasing an air receiver tank, it’s essential to ensure that it meets industry standards and regulations. In the United States, tanks with a volume over 125 gallons must be built to ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) standards. Other certifications or approvals may also be required depending on your location and industry.
Additionally, regular inspections by a certified professional may be required to ensure the tank is in safe working condition. This can also help identify and address any potential issues before they become serious problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do air receiver tanks rust?
Air receiver tanks are prone to rust due to constant exposure to moisture and compressed air. It’s essential to regularly drain the tank and properly maintain it to prevent rust.
How often should an air receiver tank be drained?
This depends on various factors such as humidity levels, usage, and tank size. It’s recommended to drain the tank at least once a day or after every use. However, it’s best to consult the tank manufacturer for precise guidelines on draining frequency.
Can I install an air receiver tank outdoors?
Yes, but it’s crucial to consider environmental factors such as temperature and moisture levels. Exposure to extreme temperatures or high humidity levels can affect the tank’s performance and potentially lead to corrosion or rust.
Can I install an air receiver tank myself?
It’s recommended to have a professional installer or technician set up the air receiver tank to ensure it’s done correctly and safely. Proper installation is crucial for the tank’s performance and longevity, as well as the safety of those using it.
Conclusion
Air receiver tanks play a crucial role in many industries, providing compressed air for various applications. However, it’s important to understand their potential hazards and take appropriate safety measures to prevent accidents and damage. Regular maintenance, monitoring, and compliance with regulations are key factors in ensuring the safe operation of air receiver tanks.
By understanding their function, components, and regulations, you can make informed decisions when purchasing and using an air receiver tank for your specific needs. So, it is necessary to keep the aforementioned points in mind while working with air receiver tanks to ensure safety and efficiency in operations.

